Metal ingots / milled surface / AxBxT configurable / mild steel, tool steel, stainless steel / normalised
- Order quantities extended (D-JIT)
Part Number
Once your search is narrowed to one product,
the corresponding part number is displayed here.
- Drawing / Specifications
- 3D Preview 3D preview is available after complete configuration
- Part Numbers
- More Information
- Catalog
- Technical Information
Back to the Category Material Plates, Blocks
Technical Drawing - Metal Ingots
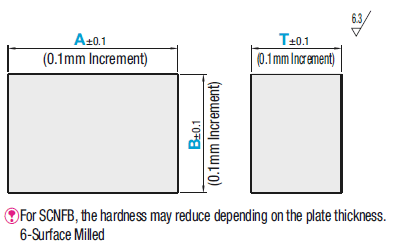
Open the technical drawing in the new window
Available dimensions and tolerances can be found under the tab More Information.
Basic Properties (e.g., material, hardness, coating, tolerance) - Metal Ingots
| Part Number | Material | Hardness |
| SSFB | EN 1.0038 Equiv. | - |
| SCFB | EN 1.1206 Equiv. | - |
| SCNFB | EN 1.1206 Equiv. Thermal Refined | 25±3HRC |
| SCFF | EN 1.4305 Equiv. | - |
| SCFS | EN 1.4301 Equiv. | - |
| Item | EN 1.0038 Equiv. EN 1.1206 Equiv. EN 1.1206 Equiv. Thermal Refined | EN 1.4305 Equiv. EN 1.4301 Equiv. | |
| Thickness Parallelism (per 100mm) | 0.02 | 0.05 | |
| Flatness (per 100mm) | T1.5~7.9 | 0.04 | 0.1 |
| T8~15.9 | 0.07 | ||
| T16~ | 0.05 | ||
| Perpendicularity (Each Plane) | 0.02 per 100mm | ||
| Circumference Chamfering | C0.5 or Less | ||
Further specifications can be found under the tab More Information .
Composition of a Product Code - Metal Ingots
| Part Number | - | A | - | B | - | T |
| SCFB | - | 30.5 | - | 20.6 | - | 17.1 |
General Information - Metal Ingots

Selection details of flat steels/plates (metal)
- Material: aluminum, steel, tool steel, pre-hardened steel, stainless steel (stainless steel), copper, titanium
- Surface treatment: milled, front-polished, flat-polished
- Heat treatment: annealed, normal annealed, pre-hardened, tempered, half hard, quarter hard
- Length [A]: 6 to 3000 mm in 0.01 mm increments
- Width [B]: 6 to 1500 mm in 0.01 mm increments
- Thickness [T]: 1.5 to 100 mm in 0.01 mm increments
- Parallelism: up to 0.01/100 mm
- Evenness: up to 0.01/100 mm
- Perpendicularity: up to 0.02/100 mm
Description/Basics
The metal plates from MISUMI are semi-finished products and are often used in the industry for further processing.
These can be selected in the MISUMI online shop in different versions. The machining of the lateral surfaces, or rolled, milled or ground at the top and the bottom, is available for the metal plate. The metal plates are available in various tolerances. This usually depends on the respective surface machining. This allows you to configure the MISUMI metal plates to suit your needs and use them as a semi-finished product for further processing. A customized metal block or metal plate can help to reduce the number of work steps in your further processing of the metal plate.
The metal plates can therefore be used well as semi-finished products for further processing, or often serve as a base plate for substructures, as well as column guide frames.
An overview of the different metal plates can be found in the PDF Metal Plate Overview.
You can find other shapes and materials of the semi-finished products by following this link.
MISUMI also offers the service to manufacture metal plates according to your needs with meviy by uploading CAD data.
Aluminum Plate
The aluminum plate as a blank or raw material from MISUMI is light compared to other materials, but stable and shock resistant. Therefore, the material aluminum is very often used as a Aluminium Extrusions in plant and mechanical engineering.
Aluminum plates exhibit good corrosion resistance despite the lack of surface treatment. In principle, aluminum forms an oxide layer that prevents further corrosion. Aluminum plates are very good for further processing.
Steel Plate
Steel plates made of structural steel are inexpensive in terms of their ratio and also economical due to their good workability.
The steel plate offers high strength and density. Steel has long been a very common material, so there are many types of steel suitable for different technical requirements.
Alloy tool steel has a higher temperature resistance, resistance, and hardness than usual structural steel. Another major advantage of this steel plate is the possibility of hardening and remuneration of the material.
One disadvantage of steel plates is the rather poor corrosion resistance. Without a subsequent surface treatment, steel tends to quickly corrode.
Stainless Steel Plate
The MISUMI stainless steel plates have good to very good corrosion resistance, which makes the material durable. MISUMI offers various stainless steel plates for a wide variety of requirements in plant and mechanical engineering.
The surface of stainless steel can be visually refined by sanding or polishing. Stainless steel plates have good temperature resistance, but stainless steel can stain at high temperatures (tempering colour). This should be taken into account for welding joints.
Stainless steels with chrome-nickel content have an antibacterial effect and offer a poor substrate for germs when polished, which also makes the stainless steel plate hygienic.
Copper Plate/Brass Plate
The copper plate has very good thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. This represents a special feature for other materials. Copper plates also have good corrosion resistance and are resistant.
MISUMI offers various copper alloys in its product range. The most commonly used copper is cold-solidified copper due to its good electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity.
Another variant of the copper plate is MISUMI made of oxygen-free copper, which is also known as pure copper. Oxygen-free copper has good resistance to hydrogen embrittlement and is often used in the electrical industry.
Chrome copper plates offer good mechanical strength and abrasion resistance at high temperatures.
The brass plate, on the other hand, offers high strength and ductility. Therefore, brass permits plastic deformation before the material has a fatigue fracture.
Titanium Plate
Titanium plates from MISUMI can be referred to as pure titanium.
The titanium plate is light, but it has a high strength and very high corrosion resistance. Titanium plates also have very good biocompatibility. Since the titanium plates are also biologically compatible, this material is frequently represented in medical technology. Due to its low weight and high strength, titanium is also often used in lightweight construction such as aerospace and aviation. The possible application spectrum of titanium is large. However, titanium plates are usually only used if the properties such as strength of aluminum, for example, are no longer sufficient. The reason for this is that titanium is more cost-intensive in comparison, since production causes a high energy consumption. However, the combination of the good properties of titanium is required for many applications and applications.
Additional properties of the various materials can be found in the PDF of the Metal Plate Properties.
On-demand Manufacturing

With meviy, MISUMI also offers to manufacture metal plates and sheet metal according to your wishes. Simply upload the CAD data.
Industrial Applications




Part Number:
- In order to open the 3D preview, the part number must be fixed.
3D preview is not available, because the part number has not yet been determined.
Part Number
|
|---|
| SCFB-[10-500/0.1]-[10-200/0.1]-[1.5-100/0.1] |
| SCNFB-[10-200/0.1]-[10-200/0.1]-[1.5-60/0.1] |
| SSFB-[10-500/0.1]-[10-200/0.1]-[1.5-100/0.1] |
| Part Number | Minimum order quantity | Volume Discount | RoHS | Finish Method | Material | Thickness T (mm) | Length A (mm) | Width B (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 Days | 10 | 6-Surface Milling (6F) | [Carbon Steel , Chrome Molybdenum Steel] EN 1.1206 Equiv. | 1.5 ~ 100 | 10 ~ 500 | 10 ~ 200 | ||
| 1 | 7 Days | 10 | 6-Surface Milling (6F) | [Carbon Steel , Chrome Molybdenum Steel] EN 1.1206 Equiv. Thermal Refined | 1.5 ~ 60 | 10 ~ 200 | 10 ~ 200 | ||
| 1 | 8 Days | 10 | Upper-Lower Surface Rotary Grinding (4F2RG) | [Carbon Steel , Chrome Molybdenum Steel] EN 1.0038 Equiv. | 1.5 ~ 100 | 10 ~ 500 | 10 ~ 200 |
Loading...
Back to the Category Material Plates, Blocks
Technical Drawing - Metal Ingots

Specification Tables - Metal Ingots
| 0.1mm Increment | T: 0.1mm Increment | |||||
| A | T B | 1.5~9.9 | 5.0~9.9 | |||
| SSFB | SCFB | SCNFB | SCFF | SCFS | ||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 10.0~60.0 | |||||
| 60.1~100.0 | ||||||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 60.1~100.0 | - | - | |||
| 60.1~100.0 | - | - | ||||
| 0.1mm Increment | T: 0.1mm Increment | |||||||||||||||
| A | T B | 10.0~20.0 | 20.1~30.0 | 30.1~40.0 | ||||||||||||
| SSFB | SCFB | SCNFB | SCFF | SCFS | SSFB | SCFB | SCNFB | SCFF | SCFS | SSFB | SCFB | SCNFB | SCFF | SCFS | ||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 10.0~60.0 | |||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | 20.0~60.0 | - | - | - | ||||||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 60.1~100.0 | |||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 100.1~130.0 | |||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 130.1~160.0 | |||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 160.1~180.0 | |||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 180.1~200.0 | |||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||
| 0.1mm Increment | T: 0.1mm Increment | ||||||||||||||||||
| A | T B | 40.1~50.0 | 50.1~60.0 | 60.1~70 | 70.1~80 | 80.1~90 | 90.1~100 | ||||||||||||
| SSFB | SCFB | SCNFB | SCFF | SCFS | SSFB | SCFB | SCNFB | SCFF | SCFS | SSFB | SCFB | SSFB | SCFB | SSFB | SCFB | SSFB | SCFB | ||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 10.0~60.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | 20.0~60.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 60.1~100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 100.1~130.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 130.1~160.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 160.1~180.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 10.0~ 60.0 | 180.1~200.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 60.1~ 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 100.1~ 130.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 130.1~ 160.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 160.1~ 180.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 180.1~ 200.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 200.1~ 250.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 250.1~ 300.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 300.1~ 350.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 350.1~ 400.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 400.1~ 450.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| 450.1~ 500.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
Configure
Basic Attributes
-
Finish Method
-
Thickness T(mm)
-
Length A(mm)
-
Width B(mm)
-
Type
- SCFB
- SCFF
- SCFS
- SCNFB
- SSFB
-
Material
- Carbon Steel , Chrome Molybdenum Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Carbon Steel , Chrome Molybdenum Steel
-
Filter by CAD data type
- 2D
- 3D
Filter by standard shipping days
-
- All
- 7 Days or Less
- 8 Days or Less
Optional Attributes
- The specifications and dimensions of some parts may not be fully covered. For exact details, refer to manufacturer catalogs .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Question:
Is 1.4301 magnetic?
-
Answer:
The material EN 1.4301 is austenitic and is therefore not considered magnetic. This is fundamentally due to the austenitic structure. However, there are also ferritic or martensitic stainless steel types (stainless steel) that are magnetic. Here, magnetism and corrosion resistance are often shared.
-
Question:
What is the advantage of titanium?
-
Answer:
Titanium has a high strength that lies in the area of stainless steel. However, titanium has a lower density (4.51 g/cm³) and is therefore lighter. Titanium is also very corrosion-resistant because it forms its own oxide layer as a protective layer. This layer protects the material from corrosion, but also from other influences.
-
Question:
Can aluminum corrode?
-
Answer:
Aluminum is considered rust-free and generally does not corrode. Aluminum forms a thin oxide layer if exposed to oxygen, which protects the underlying aluminum from further oxidation. The oxide layer serves as a protective layer, which the material form independently and replicates it when it is removed.
-
Question:
Does oxygen-free copper corrode?
-
Answer:
As a rule, copper does not rust, because pure copper does not contain any iron. Copper forms a green oxide layer that protects the material underneath. This protective layer is also called patina or verdigris. However, if copper comes into contact with low ph levels (below 6), further decomposition (pitting) of the material may occur.
Complementary Products
Tech Support
- Technical Support
- Tel:+49 69 668173-0 / FAX:+49 69 668173-360
- Technical Inquiry











