- Estoque
- Mostrar apenas artigos em stock
- Tip O.D.(mm)
- 17
- Material
- Steel
- EN 1.7220 Equiv.
- Hardness
- Surface Treatment
- H Dimension Specifying Method
- Type
- CAD
- 2D
- 3D
- Dias de envio estimados
- Tudo
- Envio possível no próprio dia
Stopper bolts / spherical design / H standard (BSTEH17)
Desenho de contorno e tabela de especificações
Back to the Category Stopper Bolts
Technical Drawing - Stopper Bolts
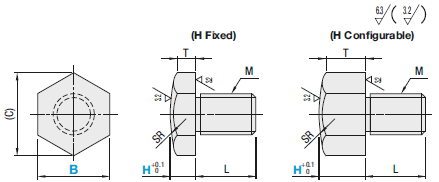
Open the technical drawing in the new window
Available dimensions and tolerances can be found under the tab More Information.
Basic Properties (e.g., material, hardness, coating, tolerance) - Stopper Bolts
| H | Type | Material | Hardness | Surface Treatment |
| Fixed | BSTEH | EN 1.7220 Equiv. | 46~50HRC | Electroless Nickel Plating |
| SBTEH | EN 1.4037 Equiv. | 50~55HRC | - | |
| Configurable | BSTFH | EN 1.7220 Equiv. | 32~38HRC | Electroless Nickel Plating |
| SBTFH | EN 1.4037 Equiv. | 40~45HRC | - |
Further specifications can be found under the tab More Information.
Composition of a Product Code - Stopper Bolts
| Part Number | - | H | |
| (H Fixed) (H Configurable) | BSTEH10B SBTFH8 | - | 8.5 |
Informações detalhadas
Informações básicas
Cuidado
- Dear Customers: All products are available from May 18th only with an extended lead time.
Contorno e especificações
Back to the Category Stopper Bolts
Technical Drawing - Stopper Bolts

Specification Tables - Stopper Bolts
| Part Number | H | M (Coarse) | L | (C) | T | SR | Unit Price | ||
| Type | B | BSTEH | SBTEH | ||||||
| BSTEH SBTEH | 5.5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 6.4 | 4.3 | 7.5 | ||
| 7 | 4 | 8.1 | 4 | 8.5 | |||||
| 8 | 5 | 6 | 9.2 | 3.9 | 10 | ||||
| 10 | 8 | 6 | 11.5 | 6.5 | 12 | ||||
| 10B | 9 | ||||||||
| 13 | 8 | 10 | 15 | 6.1 | 16 | ||||
| 14 | 16.2 | 6.1 | 18 | ||||||
| 14B | 12 | ||||||||
| 17 | 10 | 10 | 19.6 | 7.7 | 22 | ||||
| 19 | 12 | 15 | 21.9 | 7.5 | 25 | ||||
| 19B | 18 | ||||||||
■H Configurable
| Part Number | H 0.5mm Increment | M (Coarse) | L | (C) | T | SR | Unit Price | ||
| Type | B | BSTFH | SBTFH | ||||||
| BSTFH SBTFH | 5.5 | 2.0~10.0 | 3 | 5 | 6.4 | H-0.7 | 7.5 | ||
| 7 | 4 | 8.1 | H-1 | 8.5 | |||||
| 8 | 5 | 6 | 9.2 | H-1.1 | 10 | ||||
| 10 | 5.0~30.0 | 6 | 11.5 | H-1.5 | 12 | ||||
| 13 | 8 | 10 | 15 | H-1.9 | 16 | ||||
| 14 | 16.2 | H-1.9 | 18 | ||||||
| 17 | 10.0~50.0 | 10 | 12 | 19.6 | H-2.3 | 22 | |||
| 19 | 12 | 15 | 21.9 | H-2.5 | 25 | ||||
General Information - Stopper Bolts

Stop bolt selection details
- Material: steel, stainless steel
- Coatings: uncoated, nickel-plated
- Hardness: 32 to 55HRC
- Wrench width: 3 to 20 mm
- Head height: up to 50 mm
- Threads: M3 to M12
- Head diameter: 5 to 20 mm
- Diameter mounting side: 2 to 12 mm (m6)
- Brush head: polyurethane rubber (PUR) with Shore A90
Description/Basics
The stopper bolt from the group of stopper elements serves primarily as a stop in mechanical engineering (collision protection). In addition, it is increasingly used to determine the final position for workpieces and in movable applications in device construction (e.g., workpiece carriers).
In principle, MISUMI offers two mounting variants of the stop bolts. The commercially available variants are threaded stop bolts. Threaded stopper bolts have the advantage that they are easy to assemble and disassemble. Furthermore, the thread of the stop bolt can be used to adjust the spacing and the end position.
In addition, MISUMI offers non-threaded stop bolts for pressing in with fit tolerance as a further assembly variant. These stop bolts can also be inserted into the component to be moved in the event of frequent collisions to protect the component. In order to strengthen the component protection, the different designs of the stop bolts can also be combined with one another.
The undercuts at the transition from the shaft to the head ensures that in the event of impact energy can be transferred to the support surface over as large an area as possible.
As a rule, stop bolts have a flat contact surface. Correct alignment is necessary so that the entire contact surface can be used. If exact alignment is not possible, MISUMI also offers stop bolts with a spherical contact surface.
Both variants of stop bolts are protected from increased wear or damage with a hardened (tempered) contact surface. A low-wear stop bolt is necessary, especially with high cycles and frequent collisions. The stop bolts are also available with a cushioned contact surface made of polyurethane rubber. These can reduce the shock impulse, vibrations and associated noise.
If there is only a limited installation space, MISUMI offers the special form with a key hole on the head side. This facilitates the adjustment and installation of the stop bolt even when access is difficult.
Threaded stopper blocks are suitable for fastening stop bolts that have a configurable height.
Alternatively, MISUMI offers a large number of stopper bolts with brush heads and dampers, which, contrary to the stop bolt, have primarily damping properties.
If component guidance is required in addition to rigid and precise positioning, a height adjusting pin with a collar can serve as a guided stopper.
Application examples
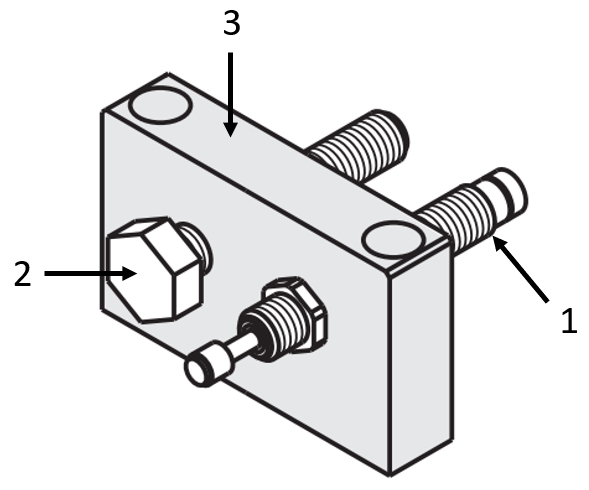
Application example – end stop with threaded stop bolt
(1) Adjustable shock absorber, (2) Stop bolts, (3) Threaded Stopper Block
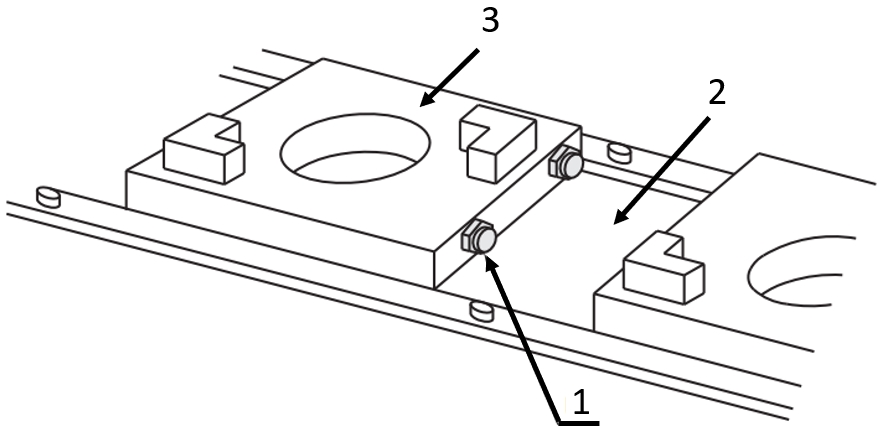
Application example – workpiece carrier with stop bolt
(1) Stop bolt with rubber, (2) ฺBelt conveyor, (3) Workpiece carrier
Industrial Applications




